Abstract:
Odontomas are the most common odontogenic benign tumor originating from an alteration of differential mesenchymal and epithelial odontogenic cells; it is the capacity of forming enamel, dentin, cement, and pulp { Susana Amado Cuesta }. Classified as a 2 category Complex and Compound types. They are usually diagnosed as routine dental radiographs. Healthy 27 years old female patient attended our clinic to complain of dull pain in the left mandible area. A diagnostic radiograph revealed Odontoma is present. Surgical enucleation is recommended, to avoid disturbing nearby structures. Early detection is a good prognosis.
Introduction:
Odontomas are one of the most common odontogenic tumors.
Analyzed records of 527 odontogenic tumors in the institute of Oncology, University of Istanbul, from 1971 to 2003.The most common lesions were ameloblastomas (n=133),odontomas (n=109),odontogenic myxomas(n=83) and others.{ V Olgac,B G Koseoglu } Records of the Department of Oral Medicine and Pathology, Dental School, University of Athens, total 652 cases of odontogenic tumors reported, from 1970 to 2011.They were keratocystic lesions (52.7),odontoma (18.9),ameloblastoma (16.1).{ Evanthia Chrysomali 1} January 2015 to December 2015 and analyzed 2167 digital panoramic radiographs from the database of a Specialized Dental Radiological Clinic in Belo Horizonte, Brazil.Seven images presented odontomas,prevalence rate was (0.32%).{ Leonardo Santos Leal }
There is no history of reported cases or research about odontoma in our country. That is why we chose this case.
The term odontoma was originally used by Paul Broca in 1867 to describe all odontogenic tumors. Odontomas are more often in the permanent dentition. The lesions tend to be located between the roots of erupted teeth or between the deciduous and permanent teeth. Anterior maxilla and posterior mandible are the most common locations for complex odontoma, compound odontomas are usually found in the anterior maxilla, this case report presents an unusual case of compound odontoma located in the anterior mandible.
Presently the World Health Organization (WHO) classifies odontoma within the category of odontogenic tumors (OT) composed of epithelium and odontogenic ectomesenchyme with or without the formation of mineralized dental tissues. Later on, in 1946 Thoma HM and Goldman HM formulated a presently discussed odontoma classification. Odontomas are classified taking into account the organization and degree of alteration of odontogenic cells, these are two classifications compound (CPO) and complex (CO).
A compound odontogenic tumor (CPO) exhibits morphological and histological differentiation and a varied number of tooth-like structures are present. While complex
an odontogenic tumor (CO) only presents histological differentiation (enamel, dentin, and cementum are disorganized) {11}.
Several factors are included in the pathogenesis of odontomas. It could be due to trauma during primary dentition, as well as to inflammatory and infectious processes, hereditary anomalies (Gardner’s syndrome, Herman’s syndrome), odontoblastic hyperactivity, or alteration of the genetic components responsible for controlling dental development.
Radiologic characteristics:
According to the degree of odontoma classification, these stages of development can be identified. In the first stage, the lesion appears radio lucid (due to lack of calcification of dental tissues). The intermediate stage is characterized by partial calcification and the final odontoma appears radiopaque and surrounded by a radiolucent halo.
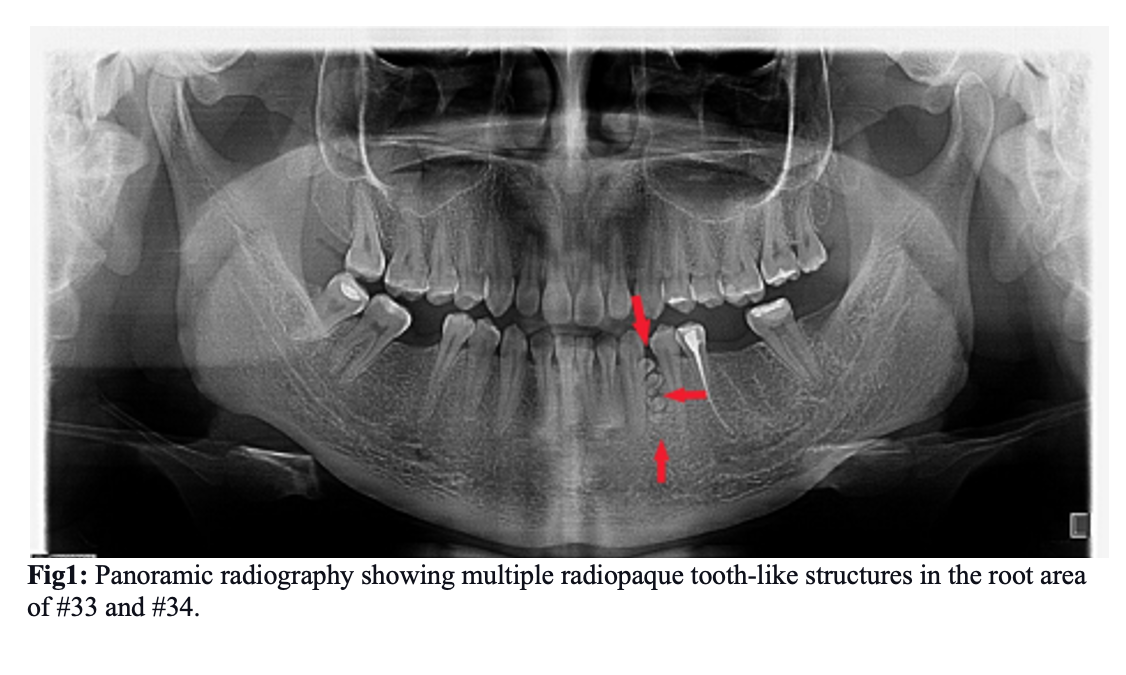
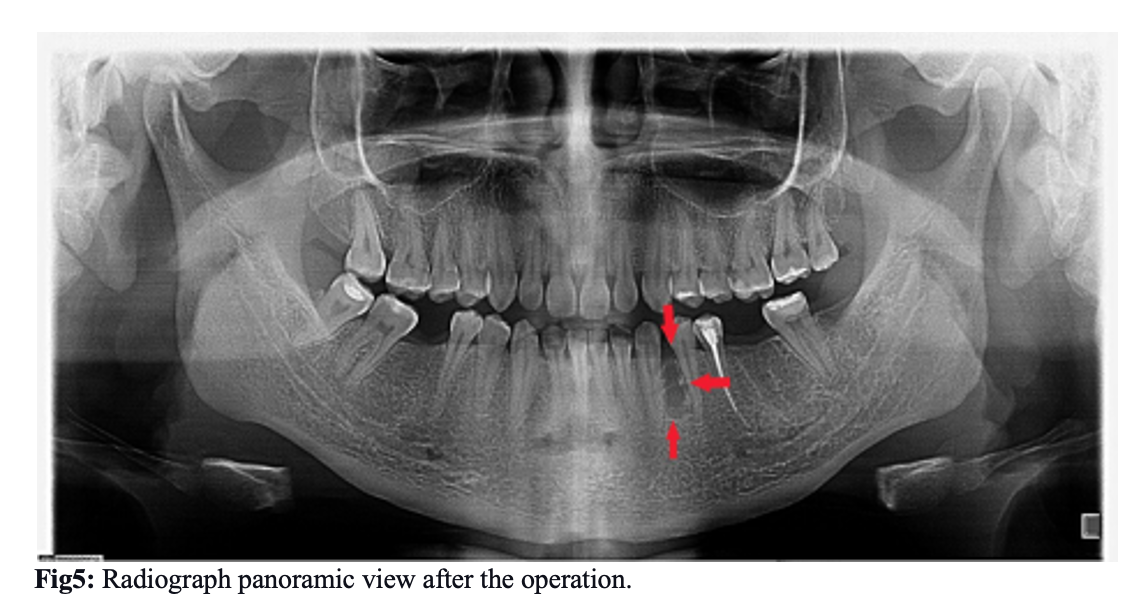
In our case patient showed on radiograph: #37 and #48 had a filling, #36 and #46 extracted many years ago, #35 root canal treatment was made. Then multiple full calcified radiopaque tooth-like structures surrounded by radiolucent halo were seen between #33 and #34. There are other abnormalities not seen.
Case report:
A healthy 27-year-old female patient attended our dental clinic appointment with doubts about the apparent space between #33 and #34 (#34 displaced distally) and complained of soft dull pain during last month. Intra-oral examination revealed normal dentition with the healthy oral environment, #35 had an old filling, #36 and #46 was missed, 2-4mm abnormal space appeared between the #33 and #34. Initially, the provisional diagnosis was periodontitis due to the old filling of #35.
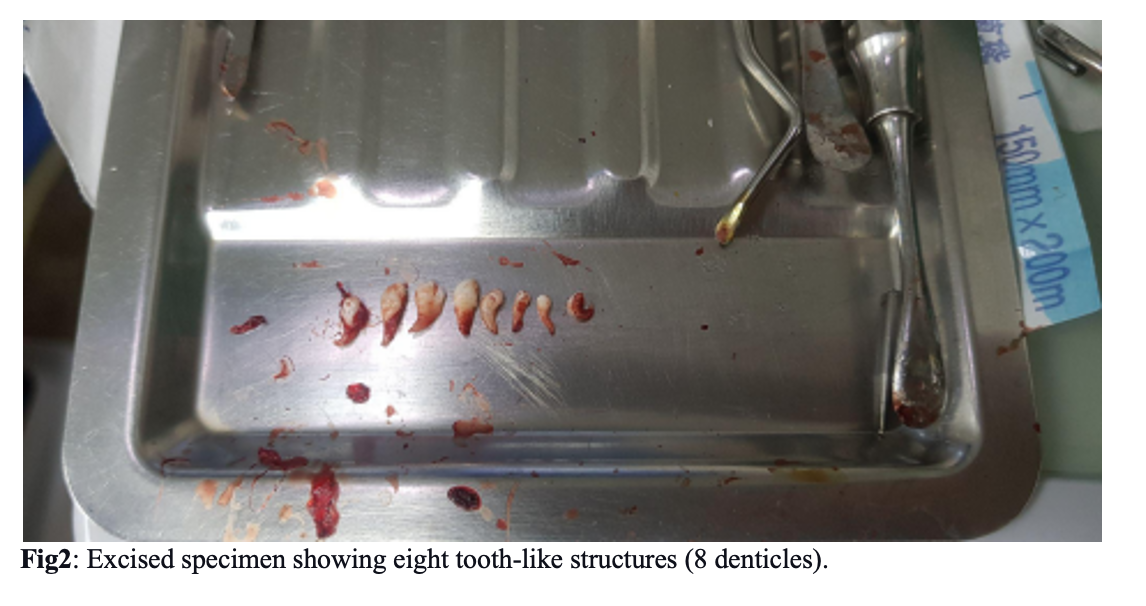
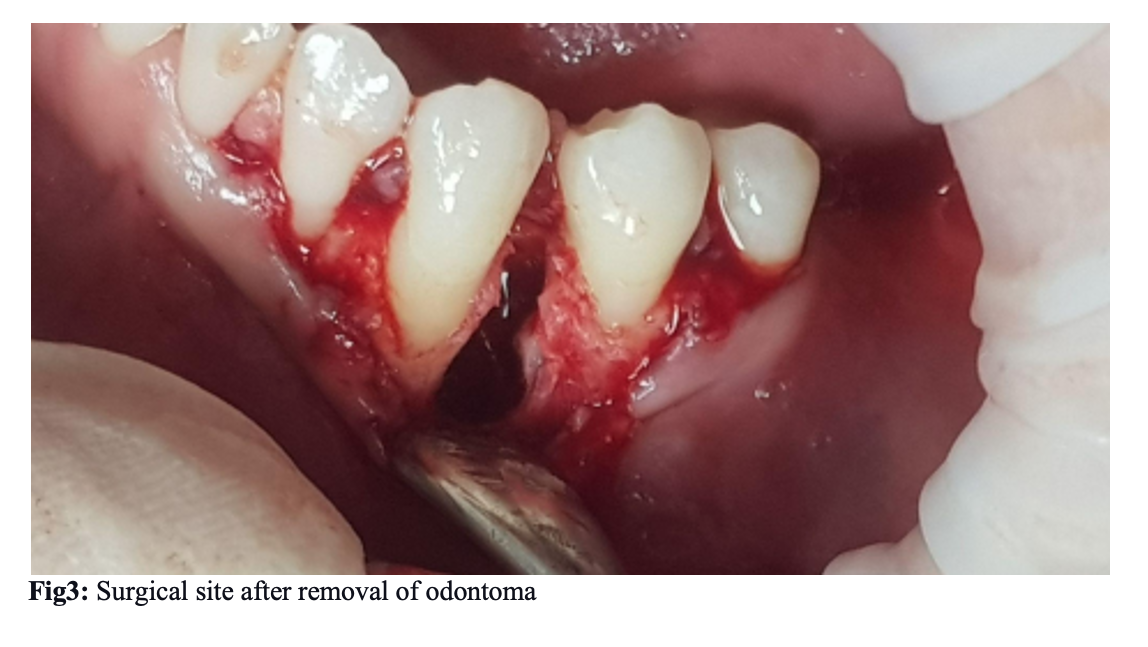
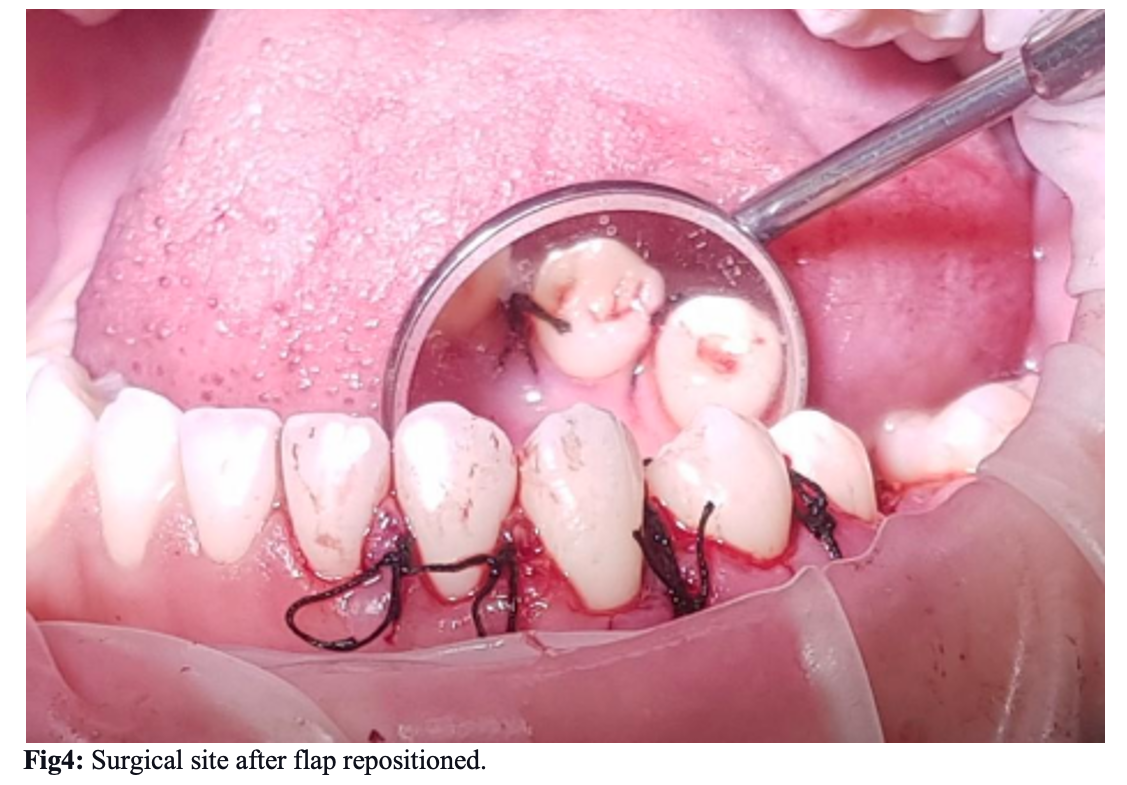
Diagnostic radiograph in panoramic view (Fig.1) revealed the presence of multiple small radiopaque tooth-like structures in the root region of #33 and #34, surrounded by a narrow radiolucent area. This led to the diagnosis of compound odontoma. Then surgical enucleation planned under local mandibular anesthesia on the dental chair was discussed with our patient. Under local mandibular anesthesia (1 cartridge: lidocaine 2%, epinephrine 1:100.000), perioral regions of #33 and #34 to expose the bone with envelope flap incision between #31 to #35 (Fig.3). Envelope flap incision provides adequate soft tissues covering for any bone defects and has a wider base, assuring vascularity up to the wound margins. A bone window was made between #33 and #34 using a straight low-speed handpiece bearing a round carbide bur under normal saline irrigation. Denticles were exposed, a total of eight denticles of various sizes and shapes were removed along with the follicle excavated using a thin elevator (HU-FRIEDY CL-87) with a curette(LY-019) (fig4). After thorough 20ml saline irrigation of the enucleated site, a blood clotting sponge is put on the base of the wound, it helps to blood form and clot. The flap is repositioned and interrupted suturing with 4-0 Black silk. There was no evidence of visible infection. But prophylactic antibiotics are prescribed.
Rp:Amoxicillin 500mg Rp:Ibuprofen 400mg DtdN:9 in tab DtdN:6in tab
S:3 times in a day, during 3 days. S: for mild discomfort 1tab,6 to 8 hours after a meal.
Postoperative recommendations are given:
- Do not rinse or spit for 24 hours after surgery
- Keep your finger and tongue away from the surgical area
- Use ice packs on the surgical area (side of the face) for the first 48 hours (apply ice 20 minutes on and 10 minutes off)
- Drink plenty of fluids (Do not use a straw-it creates suction in the mouth that could cause complications)
- Do not exercise at least 3 to 4 days after surgery
- After the first postoperative day, use a warm salt water rinse following meals for the first week to flush out particles of food and debris that may lodge in the surgical area. -Diet should consist mainly of soft, easily swallowed foods and cool drinks. Avoid anything that might get stuck in your teeth, no seeds, nuts, rice, popcorn, or similar foods. -Suture removal is 10 days after.
The patient had already planned to go abroad after 5 days of surgery. Then we could not recall her.


Discussion:
Most of these lesions are asymptomatic and are usually detected on routine radiograph { Seo-Young An }{8}or in some rare cases odontomas have acute or chronic symptoms due to infection. Several case series have documented that the majority of all odontomas were diagnosed in the first two decades of life { Lucia Thistle Barba }. Although they may be discovered at any age, no gender differentiation { Susana Amado Cuesta }, less than 10% are found in patients over 40 years old. Some studies have reported a correlation between patients age and the types of odontoma involved compound lesions being more frequent in younger patients { Seo-Young An } Treatment of choice of the odontoma is enucleation, then fixing displaced teeth, in some other cases allow the eruption of permanent tooth { Helena Salgado } and remove to complain of pain. These tooth-like structures were carefully excised under local anesthesia without disturbing neighboring structures. After enucleation, we recommended orthodontic treatment for the displaced tooth. But 3 months are required for bone healing before orthodontic treatment. Studies have shown that compound odontomas
are seen more frequently in the anterior maxilla { Malays J Med Sci }. In the present case, odontoma was found in the anterior mandible { Malays J Med Sci }{Iounnis Latrou}, which is an uncommon site of occurrence. Odontomas have a greater frequency to arise in the region of incisors and canines, which is confirmed in our case.
The prognosis is generally favorable. Early detection is helpful to avoid further complications.
Some of the complications that might arise are following impacted teeth, nasal obstruction, otodental syndrome, calcifying odontogenic cyst, or dentigerous cyst. In exceptional cases, spontaneous eruption of odontoma into the mouth occurs, accompanied by the possibility of eliciting pain. Differential diagnosis must be established with lesions such as focal residual osteitis, cementoma, calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor, adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, supernumerary tooth, cementing fibroma, or benign osteoblastoma.
Conclusion:
Panoramic examination during the first and second decade of life might be beneficial for the early detection and better prognosis for odontomas. if possible, necessary to recall and control the patient.
References:
- Susana Amado Cuesta, Jordi Gargallo Albiol, Leonardo Berini Aytes Gosme Gay Escoda.(2003). Review 61 cases of odontoma presentation of an erupted complex odontoma.8(5)
- 73-366. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14595262/
- Gabriel Serra-Serra, Leonardo Berini Aytes, Gosme Gay Escoda.(2009). Erupted odontomas: A report of these cases and review of the literature. 14(6)
- 299-303. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19300370/
- Seo-Young An, Chang Hyeon An, Karp Shik Choi.(2012). Odontoma: a retrospective study of 73 cases. 42(2)
- 77-81. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3389053/
- Helena Salgado, Pedro Mesquita.(2012). Compound odontoma-Case report 54(3)
- 161-165. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259163896_Compound_odontoma-Case_report
- Malays J Med Sci.(2017).Compound odontoma in anterior mandible-a case report.24(3)
- 92–95. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2017.24.3.11
- Ioannis Latrou, Emmanouil Vardas, Nadia Theologie-Lygidakis, Minas Leventis.(2010).A retrospective analysis of the characteristics, treatment, and follow-up of 26 odontomas in Greek children.52(3)
- 47-439. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20881338/
- Julia Yu-Fong Chang 1, Jeng-Tzung Wang, Yi-Ping Wang, Bu-Yuan Liu, Andy Sun, Chun-Pin Chiang. (2003). Odontoma: a clinicopathologic study of 81 cases Meta-Analysis of the epidemiology and clinical manifestations of odontomas.102(12)
- 82-876. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14976568/
- Peter R Morgan.(2000).Odontogenic tumors: A review.57
- 160-176. http://www.patologiabucal.com/index_htm_files/Tumores%20odontogenicos.pdf
- Lucia Thistle Barba,Daniela Muela Campos, Martina M Nevarez Rascon, Victor A Rios Barrera, Alfredo Nevarez Rascon.(2016).Descriptive aspects of odontoma, literature review.20(4)
- 265-269. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1870199X16300702
- Damla Torul, Metahan Keskin, Seda Gun, Didem Odabasi.(2018).Complex and compound odontoma: A rare clinical presentation 22(1)
- 2215-3411. https://www.scielo.sa.cr/scielo.php?pid=S2215-34112020000100023&script=sci_arttext
- Nelson BL, Thompson LD.(2010).Enucleation of mandibular complex odontoma: A report of clinical case Compound odontoma. Head Neck Pathol.4(4)
- 290-291. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2996496/
- V Olgac,B G Koseoglu, N Aksakalli.(2006).Odontogenic tumors in Istanbul: 527 cases. 44(5)
- 8-386. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16182417/
- 13. Evanthia Chrysomali 1, Minas Leventis, Savas Titsinides, Vasileios Kyriakopoulos, Alexandra Sklavounou.(2013).Odontogenic tumors.24(5).
- 5-1521. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24036718/
- Leonardo Santos Leal,Daniel Pardini,Samuel Mendes Teixeira,Leonardo Oliveira Buzatti.(2019)A Prevalence Study of Odontomas in a Brazilian Population.13(6).
Oral and Maxillofacial surgery department(2021)
Resident doctors: B.Enkhzul
Ts.Khaliunsuren
E.Bolor